Greedy Algorithms
Divide and Conquer
Divide and conquer is a general algorithm design paradigm: divide the problem into smaller subproblems, solve the subproblems recursively, and then combine the solutions to the subproblems to solve the original problem.
Largest pair sum in an unsorted array
Given an unsorted of distinct integers, find the largest pair sum in it. For example, the largest pair sum in {12, 34, 10, 6, 40} is 74.
Brute force solution
numbers = [2,1,0,8,15,7,-1,6]
print(numbers)
max_pair_sum = 0
for i in numbers:
for j in numbers:
if i != j:
max_pair_sum = max(max_pair_sum, i + j)
print(max_pair_sum)
# time Complexity = n^2
# space Complexity = 1
[2, 1, 0, 8, 15, 7, -1, 6]
23
Best solution
Initialize the first = Integer.MIN_VALUE second = Integer.MIN_VALUE
Loop through the elements a) If the current element is greater than the first max element, then update second max to the first max and update the first max to the current element.
Return (first + second)
def findLargestSumPair(arr, n):
# Initialize first and second
# largest element
if arr[0] > arr[1]:
first_big_number = arr[0]
second_big_number = arr[1]
else:
first_big_number = arr[1]
second_big_number = arr[0]
# Traverse remaining array and
# find first and second largest
# elements in overall array
for i in range(2, n):
# If current element is greater
# than first then update both
# first and second
if arr[i] > first_big_number:
second_big_number = first_big_number
first_big_number = arr[i]
# If arr[i] is in between first
# and second then update second
elif arr[i] > second_big_number and arr[i] != first_big_number:
second_big_number = arr[i]
return (first_big_number , second_big_number)
first, second = findLargestSumPair(numbers, len(numbers))
print(first, second)
print(first + second)
# time Complexity = n
# space Complexity = 1
15 8
23
Max subarray problem
Given an array of integers, find the contiguous subarray that has the largest sum. Return the sum.
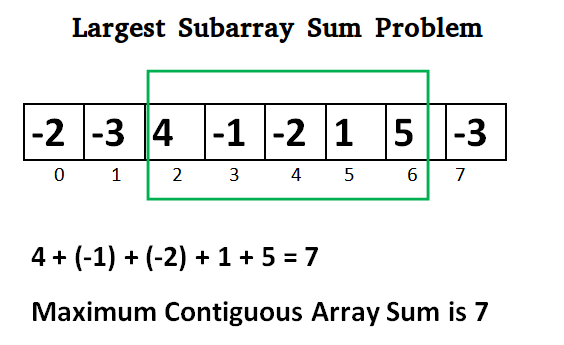
Brute force solution
Draw graph which show as stock values.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
numbers = [2,1,0,8,15,7,-1,6]
print(numbers)
x = range(len(numbers))
y = numbers
plt.title("Line graph")
plt.plot(x, y, color="red")
plt.show()
[2, 1, 0, 8, 15, 7, -1, 6]
max_contiguous_sum = 0
for index,v in enumerate(numbers):
for j in range(index ,len(numbers)):
# print(index, j)
# print(numbers[index:j+1])
max_contiguous_sum = max(max_contiguous_sum, sum(numbers[index:j+1]))
print(max_contiguous_sum)
38
Divide and Conquer solution
import sys
def maxSubArraySum(arr):
# Base case: when there is only one element in the array
if len(arr) == 1:
return arr[0]
# Recursive case: divide the problem into smaller sub-problems
m = len(arr) // 2
# Find the maximum subarray sum in the left half
left_max = maxSubArraySum(arr[:m])
# Find the maximum subarray sum in the right half
right_max = maxSubArraySum(arr[m:])
# Find the maximum subarray sum that crosses the middle element
left_sum = -sys.maxsize - 1
right_sum = -sys.maxsize - 1
sum = 0
# Traverse the array from the middle to the right
for i in range(m, len(arr)):
sum += arr[i]
right_sum = max(right_sum, sum)
sum = 0
# Traverse the array from the middle to the left
for i in range(m - 1, -1, -1):
sum += arr[i]
left_sum = max(left_sum, sum)
cross_max = left_sum + right_sum
# Return the maximum of the three subarray sums
return max(cross_max, max(left_max, right_max))
print(maxSubArraySum(numbers))
38
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
sns.set()
def max_subarray(arr):
if len(arr) == 1:
return arr[0]
else:
mid = len(arr) // 2
left = max_subarray(arr[:mid])
right = max_subarray(arr[mid:])
cross = max_crossing_subarray(arr, mid)
return max(left, right, cross)
def max_crossing_subarray(arr, mid):
left_sum = -np.inf
right_sum = -np.inf
sum = 0
for i in range(mid - 1, -1, -1):
sum += arr[i]
if sum > left_sum:
left_sum = sum
max_left = i
sum = 0
for j in range(mid, len(arr)):
sum += arr[j]
if sum > right_sum:
right_sum = sum
max_right = j
return left_sum + right_sum
arr = np.random.randint(-10, 10, 10)
arr = np.array(numbers)
max_subarray(arr)
38
def max_subarray(arr):
max_sum = -np.inf
for i in range(len(arr)):
sum = 0
for j in range(i, len(arr)):
sum += arr[j]
if sum > max_sum:
max_sum = sum
max_left = i
max_right = j
return max_sum
max_subarray(arr)
38